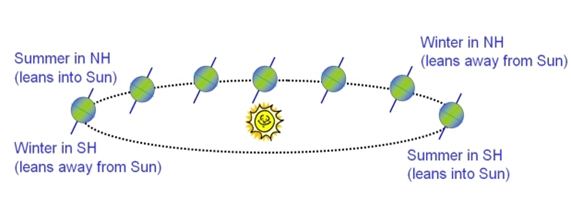
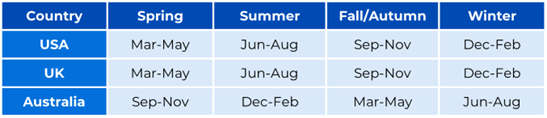
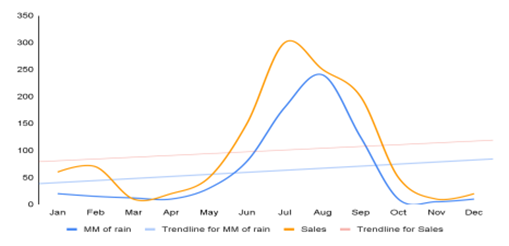
What is Forecasting?
Forecasting is the process of making predictions considering the data in the past, present, and events occurring in the future to predict the future sales, revenue, and profits of the company.
Focus on demand forecasting, after the COVID-19 pandemic, has comparatively increased. Supply chains around the world are facing major disruptions and difficulties adjusting to new demands and changing customer behavior due to lockdowns
Forecasting helps businesses improve their decision-making processes regarding risk management, cash flow, capacity planning and workforce planning as well. Better forecasting accuracy enables lower inventory levels and eventual reduction in finance and warehousing costs.
Understanding how to forecast your supply chain requirements is crucial to the success of your e-commerce store. Getting it correctly can lead to stronger supplier relationships, higher customer happiness, and more capital to help your company expand and scale.
Methods of forecasting:
In order to handle the complexities involved in developing any forecasts, many forecasting techniques have been used by businesses which suit their needs.
Selection of the right method depends on various factors like availability of past data, market demand understanding, desired accuracy in forecasting, time required in preparing the forecasts, etc.
The widely used forecasting methods can be broadly be categorized in to following two methods:
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
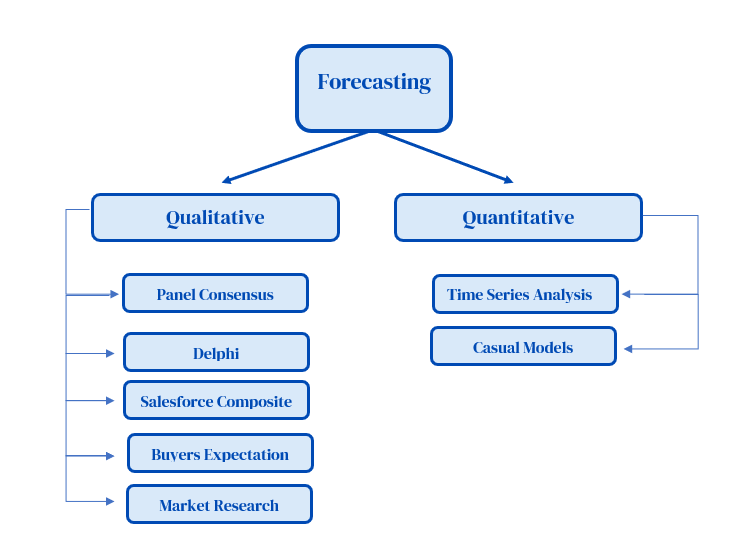
1. Qualitative Methods:
When there is a scarcity of data, qualitative sales forecasting approaches are applied. When introducing a new product to the market, for example, qualitative procedures can be used. There is insufficient information on the product to make future predictions. The techniques rely on human judgment and rating schemes to convert qualitative data into quantitative estimates. The method’s goal is to bring all of the judgments and information about the elements being estimated together logically and methodically. The following are five qualitative techniques:
- Panel Consensus: The simplest technique is panel consensus, it is based on the idea that a group of specialists in several domains may provide a better forecast than a single person. The technique is no secret, and discussion between professionals is permitted.
- Delphi Method: The Delphi method is a revenue forecasting strategy that employs surveys and questionnaires to estimate future sales. The Delphi approach aims to predict the likelihood of events occurring and the time-frame in which they will occur. The Delphi approach, like panel consensus, involves experts and a Delphi coordinator.

- Salesforce Composite:
The corporation asks its salespeople to create forecasts using the sales force composite technique. The sales reps are assumed to have direct interaction with clients and other parties in the distribution chain. As a result, they will be more educated about a product’s demand.
- Buyer’s Expectations:
You survey purchase intentions and market intents in this sales forecasting technique. If you wish to conduct a survey of buying intentions, you pick a sample of potential consumers and ask them about their future plans to acquire the goods. The entire demand projection is then calculated by extrapolating the data.
- Market Research:
Market research is a method of forecasting demand that combines both systematic and formal approaches. It entails putting real-world market theories to the test.
Advantages of Qualitative Techniques:
- Better Sales Projections
- More Flexibility in Forecasting
- Reducing Ambiguous Data
Drawbacks of Qualitative Techniques:
- Anchoring events and selective perception.
Forecasters that use anchoring events allow recent occurrences to impact their perceptions of future events.
- Selective perception:
Forecasters who use selective perception dismiss significant evidence that contradicts their idea of how the future will develop.
- Quantitative Methods:
The quantitative forecast approach employs historical data to forecast future data, particularly numerical data with a continuous pattern. This strategy is commonly used to make short-term forecasts. It is objective in character and based on mathematical models.
- Time Series Analysis
When you have years of data about a product or product line, you can utilize the Time Series analysis sales forecast technique. It can also be used when there are evident trends and relationships regarding a product that is stable. The forecaster calculates the current performance rate and rate change using historical data on the product’s performance. The basis of forecasting is the acceleration or slowing of present rates. A time-series approach is a collection of chronologically arranged raw data points. A time-series analysis can help you understand:
- Trends in the data
- Cyclical performance patterns that repeat any two or three years
- Any systematic variation or regularity of data in different seasons
- Growth rates of various trends in data.
- Causal Models
When you have adequate historical data and analysis on a product, you can create causal sales and forecasting models. The investigation should include the factors you want to forecast as well as other economic and socioeconomic aspects. The causal model should be used if you require complex sales and forecasting models. It expresses the important causal relationship and can contain information from market surveys and other factors. A time-series analysis can also be incorporated into the technique. It takes into account the flow system’s characteristics and makes predictions about connected events like promotions and strikes.
Advantages of Quantitative Methods:
- Addresses Historic Data Exposes Patterns
- Attracts Stakeholders
- Offers comprehensive projections
Disadvantages of Quantitative Methods:
- Lacks Detail
- May be difficult to interpret
- Can be Costly
What’s new?
Traditional forecasting models such where only historical data is considered are getting obsolete as a result of the increased amount of data generated from businesses and external sources. Implementation of machine learning algorithms into businesses in supply chain management companies can improve the accuracy of the forecasting results and optimize their restock cycles.
Machine learning takes demand forecasting to the next stage. It facilitates enhanced forecasts based on real time data using internal and external data sources such as weather, demographics, online reviews and social media, etc. Machine learning algorithms can easily adapt to external changes. With the help of this external data and machine learning algorithms it becomes easy to manage supply chain networks rather than managing it manually.
How we can help?
At Accurest, we believe that businessman has the most appropriate idea for the expected demands of any product either new or one which has a historical data.
For products have historical sales data, we prepare the forecasts using the available past sales data and an expected growth %. These are then revisited on frequent intervals in order to analyze the deviations from the actuals and the forecasts are then updated.
For new products, the forecasts are initially based on individual judgement of the businessman. Close monitoring is done for any newly launched products to update the forecasts at much lesser intervals. This helps in getting more accurate forecasts for such new products.